Hysterectomy
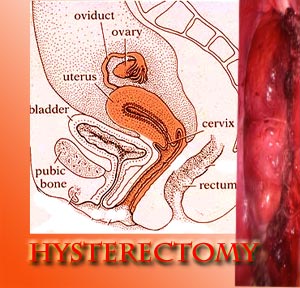
Hysterectomy is probably one of the most common surgical procedures performed on women. It involves removal of the uterus and often the ovaries and fallopian tubes too. A hysterectomy can be painful, physically and emotionally to a woman. It can bring about a sense of loss of femininity. But often it can give great relief from symptoms that were affecting the quality of life of a woman. A physician would elect to do an abdominal hysterectomy or vaginal hysterectomy depending on the individual conditions. Laparoscopic hysterectomy reduces the time of recovery from hysterectomy surgery.
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus that can sometimes save the life of a woman. Hysterectomies were usually performed abdominally or vaginally. Laparoscopic hysterectomy is also performed in some cases. Examine some of the conditions that lead to a decision of hysterectomy surgery:
Gynecological cancer: Cancer of the uterus or cervix usually necessitates removal of the uterus and cervix. The surgery is decided based on the kind of cancer and the extent of advancement of the disease. Endometrial cancer, cancer of the uterus or cervix or fallopian tubes usually requires hysterectomy surgery.
Endometriosis: In some cases of severe bleeding following endometriosis, a hysterectomy surgery is advised. This is the second leading reason for hysterectomies.
Fibroids: While most fibroid tumors can be treated by non-surgical methods, hysterectomy surgery may be the only permanent solution.
Uterine prolapse: When the uterus moves from its usual place down into the vagina, it can affect other organs such as the bladder. This can happen due to childbirth, obesity, loss of estrogen after menopause and weak pelvic ligaments and tissues.
Other reasons for going for a hysterectomy surgery range from heavy or irregular menstrual periods to dysmenorrhea. Severe pelvic inflammatory disease can sometimes necessitate a hysterectomy.
Types of hysterectomy surgery
Total hysterectomy involves removal of the cervix and uterus. It is known as Oopherectomy.
Partial hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove only the upper part of the uterus, leaving the cervix in place. This type of hysterectomy is referred to as supra cervical hysterectomy or subtotal hysterectomy.
Radical hysterectomy involves removal of the uterus, cervix, upper part of the vagina and the supporting tissues.
Hysterectomy surgery performed prior to menopause can bring about severe and prolonged symptoms as compared to natural menopause. A woman can experience bone loss, loss of libido and emotional difficulties too. Depression and anxiety are not uncommon. Some women fear that their sexual life will be affected due to the hysterectomy surgery. In cases where the length of the vagina is shortened, a woman may experience pain during sex. Many women may need hormone replacement therapy (HRT) following total hysterectomy where the ovaries are removed before menopause.
Hysterectomy vaginal
During a vaginal hysterectomy, an incision is made in the upper portion of the vagina and the uterus is removed through it. This is done in cases where the uterus is not too large as well as uterine prolapse. With vaginal hysterectomy, there won't be any external scarring. Recovery is also faster when compared with abdominal hysterectomy. This type of hysterectomy surgery can be done with laparoscopic assistance. The laparoscope is inserted into a small incision in the lower abdomen and this allows the surgeon to examine the pelvic organs. Specially crafted surgical instruments can help in detaching the uterus and removing it vaginally.
Hysterectomy recovery
Since a hysterectomy is performed under anesthesia, it could take a few hours for you to recover from the surgery and probably a few weeks to get back to your usual self. You will be observed for any signs of pain and discomfort. Some complications that can arise after hysterectomy surgery are blood clots, excessive bleeding and infection. Recovery from abdominal hysterectomy takes 4 - 8 weeks. It is essential to take plenty of rest and begin with light chores initially. Fever is noticed in some women post hysterectomy surgery. Rarely there is damage to the abdominal structure or organs. Women who have undergone vaginal hysterectomy may experience and inability to pass urine.
Following a hysterectomy, there is an increased risk of vaginal vault prolapse. This is a condition where the top of the vagina drops down due to a reduction in support structures. You can recover from a vaginal hysterectomy or laparoscopic hysterectomy faster, probably within a couple of weeks. You may return to work as soon as you have sufficient stamina and mobility.
- Try and get up and walking in a day to keep blood circulating and prevent blood clots from forming. Blood clots can occur in the large veins of the leg or lung.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects for about 6 weeks after the hysterectomy surgery.
- Eat a balanced diet with iron replacement to promote healing.
- Avoid constipation by drinking plenty of fluids
- Follow the prescribed exercise program
Call your physician should you experience increase in pain, persistent nausea or vomiting, heavy bleeding or signs of infection.
Abdominal hysterectomy
Abdominal hysterectomy is preferred when the uterus is enlarged or there are large fibroids, extensive adhesions or endometriosis. In cases of cancer of the uterus, ovaries or cervix, an abdominal hysterectomy is undertaken. Abdominal hysterectomy can be done with a vertical or bikini line incision. This incision is typically 10 - 15 cms long. The uterus and cervix is removed by cutting it off at the top of the vagina. The top of the vagina is repaired by sewing. This is called the vaginal cuff. This type of hysterectomy surgery reduces the incidence of damage to the urinary tract. But it involves a longer hospital stay and recovery time.
Hysterectomy laparoscopic
Laparoscopic hysterectomy surgery involves making three or four small incisions in the abdomen. This allows the laparoscope to enter the abdomen or pelvis. The uterus is cut up into small pieces and removed through the tubes that are inserted into the abdomen.It involves shorter hospitalization and recovery time. But it can be a costly surgical procedure when compared to traditional abdominal or vaginal hysterectomy.
Top of the Page: Hysterectomy
Tags:#hysterectomy #hysterectomy vaginal #hysterectomy recovery #abdominal hysterectomy #hysterectomy partial #hysterectomy surgery #hysterectomy laparoscopic

Enlarged Uterus
Bacterial Vaginosis
Yeast Infection
Irregular Menstrual Cycle
PMS - Menstruation
Dysmenorrhea
Hypomenorrhea
Mid Cycle Bleeding
Pelvic Organ Prolapse
Vaginal Atrophy
Cervix Cancer
Abnormal Pap Smear
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Ovulation Pain
Uterine Prolapse
Fibroid Tumor
Menorrhagia
Endometriosis Symptom
Galactorrhea
Hysterectomy
Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Menopause and Weight Gain
Premature Menopause
Surgical Menopause
Other health topics in TargetWoman Women Health section:
General Women Health

Women Health Tips - Women Health - key to understanding your health ...
Cardiac Care
Women's Heart Attack Symptoms - Identify heart problems...
Skin Diseases
Stress Hives - Red itchy spots ...
Women Disorders
Endocrine Disorder - Play a key role in overall wellbeing ...
Women's Reproductive Health
Testosterone Cream for Women - Hormone replacement option ...
Pregnancy
Pregnancy - Regulate your lifestyle to accommodate the needs of pregnancy ...
Head and Face
Sinus Infection - Nearly 1 of every 7 Americans suffer from ....
Women and Bone Care

Slipped Disc - Prevent injury, reduce pain ...
Menstrual Disorders
Enlarged Uterus - Uterus larger than normal size ...
Female Urinary Problems
Bladder Problems in Women - Treatable and curable ...
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Causes of Stomach Ulcers - Burning feeling in the gut ...
Respiratory Disorders
Lung function Test - How well do you breathe ...
Sleep Management

Insomnia and Weight Gain - Sleep it off ...
Psychological Disorders in Women
Mood swings and women - Not going crazy ...
Supplements for Women
Women's Vitamins - Wellness needs...
Natural Remedies

Natural Diuretic - Flush out toxins ...
Alternative Therapy
Acupuncture Point - Feel the pins and needles ...
Top of the Page: Hysterectomy
Popularity Index: 101,391

